Alternative Image creation based on Any-Image
Four Approaches for creating images are supported:
- default: using the compute-default or k3s-default playbooks which will create a base depending on the controller's distribution.
- Base: using a ClusterVision provided base distribution.
- Docker: using a docker based image creation approach.
- OSgrab: grab the base from a already installed node, since TrinityX 15.3.
The below sections cover examples for Base, Docker and OSgrab approaches.
Visit the Any-Image documentation for support matrix and more in-depth information regarding Any-Image.
Prerequisites
We work from the TrinityX local/cloned repo, Specifically the site directory where the other playbooks are presented. Refer to the installation documentation on how to clone TrinityX.
Base image approach for Rocky-8
Copy a compute playbook to a new one. For RedHat family distributions, compute-default.yml can be used. For other distributions, have a look at e.g. compute-ubuntu.yml or compute-opensuse.yml.
# cp compute-default.yml compute-myimage-rocky8.yml
# vi compute-myimage-rocky8.yml
Inside the compute-myimage-rocky8.yml yaml file:
- change the
image_namevariable in the pre_tasks section only, to reflect your preferred image name. - uncomment the
alternative_distributionvariable and specify to your needs. - uncomment the
alternative_image_sourcevariable and specify 'base'
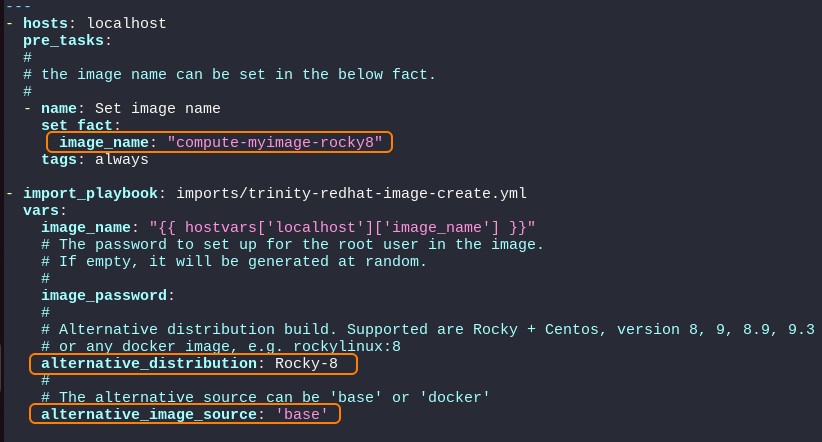
Please note the yaml format is highly sensitive to wrongfully placed spaces and tabs. It's important to 'line up' to prevent variables being ignored.
Then the playbook can be run:
# ansible-playbook compute-myimage-rocky8.yml
After the playbook finishes, the image appears in luna with the name set according to the 'image_name' variable
Docker image approach for Rocky-8
Copy a compute playbook to a new one. For RedHat family distributions, compute-default.yml can be used. For other distributions, have a look at e.g. compute-ubuntu.yml or compute-opensuse.yml.
# cp compute-default.yml compute-mydocker-rocky8.yml
# vi compute-mydocker-rocky8.yml
Inside the compute-mydocker-rocky8.yml yaml file:
- change the
image_namevariable in the pre_tasks section only, to reflect your preferred image name. - uncomment the
alternative_distributionvariable and specify to your needs. - uncomment the
alternative_image_sourcevariable and specify 'docker' - uncomment or add the
alternative_image_distrvariable and specify either 'rocky', 'almalinux', 'opensuse', 'centos' or 'ubuntu'. For RedHat family distributions, alternative_image_distr is an optional variable. If not set, the distribution will be automatically detected.
The variable alternative_image_distr is needed to ensure correct ansible var/yml includes for distribution depended configuration.
When undefined, ansible will fallback to the distribution information of the head node.
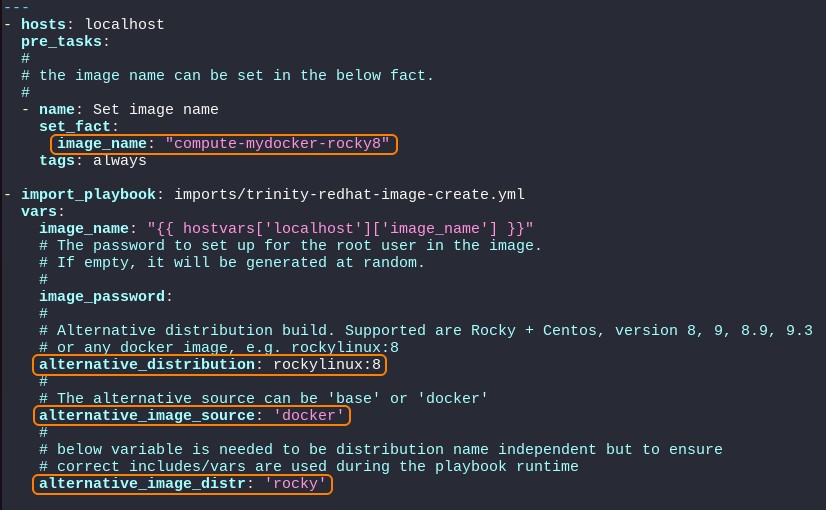
Please note the yaml format is highly sensitive to wrongfully placed spaces and tabs. It's important to 'line up' to prevent variables being ignored.
Then the playbook can be run:
# ansible-playbook compute-mydocker-rocky8.yml
After the playbook finishes, the image appears in luna with the name set according to the 'image_name' variable
OSgrabbed image approach for Rocky-8
TrinityX 15.3+
Building an image based on a already installed (a node installed outside TrinityX) compute node through grabbing the OS, is a feature that was added in TrinityX 15.3.1. Prepare luna for the OS Grab
Add an empty image that will be used to store the captured OS. The name has to be the same as supplied later in the playbook.
# luna osimage add compute-osgrabbed-rocky8
Add the node to Luna and configure its interface before grabbing.
# luna node add node-rocky8 -g compute-group -o compute-osgrabbed-rocky8
# luna node change -if BOOTIF -I 1.2.3.4 node-rocky8
# ssh-copy-id root@node-rocky8
The IP address, in the example's case 1.2.3.4, should match with what's currently configured on the installed node during step 1.
2. Perform OS Grab
Grab the system image from the node into the Luna image.
# luna node osgrab -o compute-osgrabbed-rocky8 --nodry -b node-rocky8
3. Create the required playbook
Copy a compute playbook to a new one. For RedHat family distributions, compute-default.yml can be used. For other distributions, have a look at e.g. compute-ubuntu.yml or compute-opensuse.yml.
# cp compute-default.yml compute-osgrabbed-rocky8.yml
# vi compute-osgrabbed-rocky8.yml
Inside the compute-osgrabbed-rocky8.yml yaml file:
- change the
image_namevariable in the pre_tasks section only, to reflect the earlier chosen image name, in this case 'compute-osgrabbed-rocky8'. - uncomment the
alternative_image_sourcevariable and specify 'osgrab' - uncomment or add the
alternative_image_distrvariable and specify either 'redhat', 'rocky', 'almalinux', 'opensuse', 'centos' or 'ubuntu'. Here in this example we pick 'rocky'.
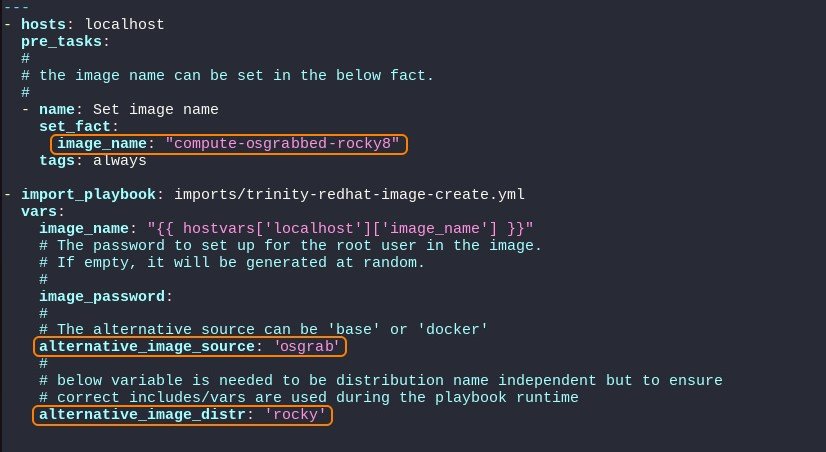
Please note the yaml format is highly sensitive to wrongfully placed spaces and tabs. It's important to 'line up' to prevent variables being ignored.
4. Run the playbook
# ansible-playbook compute-osgrabbed-rocky8.yml
After the playbook finishes, the image appears in luna with the name set according to the 'image_name' variable